Bookkeeping
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts: Components and Financial Impact

The percentage of sales method assigns a flat rate to each accounting period’s total sales. Using previous invoicing data, your accounting team will estimate what percentage of credit sales will be uncollectible. Businesses often face the challenge of customers failing to pay their debts, which can significantly impact financial health. To mitigate this risk, companies establish an allowance for doubtful accounts—a crucial accounting practice that anticipates potential losses from uncollectible receivables. While the allowance for doubtful accounts is a useful accounting method that can help assess the true value of the accounts receivable asset, it has shortfalls that need to be considered. It is impossible to know which customers will default in a given year, which makes the process inherently inaccurate.
Create allowance for doubtful accounts
The company must record an additional expense for this amount to also increase the allowance’s credit balance. The allowance can accumulate across accounting periods and may be adjusted based on the balance in the account. Ideally, you’d want 100% of your invoices paid, but unfortunately, it doesn’t always work out that way. Assuming some of your customer credit balances will go unpaid, how do you determine what is a reasonable allowance for doubtful accounts? The accounts receivable aging method uses Bookstime accounts receivable aging reports to keep track of past due invoices.

Percentage of Sales Method

The allowance for doubtful accounts is a contra-asset account that reduces the total accounts receivable reported on the balance sheet. This adjustment is necessary to reflect the realistic collectible amount, ensuring that the financial statements are not overly optimistic. This involves analyzing historical data, customer creditworthiness, and current economic conditions. The allowance for doubtful accounts, aka bad debt reserves, is recorded as a contra asset account under the accounts receivable account on a company’s balance sheet.
- Additionally, comparing trends across different economic cycles can help businesses understand how external factors, such as recessions or booms, affect their receivables.
- It helps companies present a more accurate picture of their financial position by accounting for potential losses from credit sales.
- For instance, if a business historically writes off 2% of its receivables, it might apply this rate to its current receivables to estimate the allowance.
- According to GAAP, your allowance for doubtful accounts must accurately reflect the company’s collection history.
- For example, machine learning algorithms can analyze historical data to forecast future bad debt trends, allowing businesses to adjust their strategies accordingly.
- The Pareto analysis method relies on the Pareto principle, which states that 20% of the customers cause 80% of the payment problems.
Specific identification method
Trade credit insurance is one tool to help reduce the overall impact of bad debts and secure the accounts receivable asset, thereby improving the accuracy of cash flow and P&L forecasting. All outstanding accounts receivable are grouped by age, and specific percentages are applied to each group. The sales method applies a flat percentage to the total dollar amount of sales for the period.
Financial Accounting I
Explore the components, estimation methods, and financial impact of the allowance for doubtful accounts in this comprehensive guide. It’s important to note that an allowance for doubtful accounts is simply an informed guess, and your customers’ payment behaviors may not align. When assessing accounts receivable, there may come a time when it becomes clear that one or more accounts are simply not cash flow going to be paid. By a miracle, it turns out the company ended up being rewarded a portion of their outstanding receivable balance they’d written off as part of the bankruptcy proceedings.
In this case, our jewelry store would use its judgment to assess which accounts might go uncollected. As a result, the estimated allowance for doubtful accounts for the high-risk group is $25,000 ($500,000 x 5%), while it’s $15,000 ($1,500,000 x 1%) for the low-risk group. For example, our jewelry store assumes 25% of invoices that are 90 days past due are considered uncollectible. Say it has $10,000 in unpaid invoices that are 90 days past due—its allowance for doubtful accounts for those invoices would be $2,500, or $10,000 x 25%. This provision not only helps in presenting a more accurate picture of a company’s financial status but also ensures compliance with accounting standards. Properly managing the allowance for doubtful accounts ensures that your financial statements are accurate and up-to-date.
Accounting for Holding Companies: Types, Reporting, and Strategies
This will ensure that your financial statements accurately represent the status of your company’s accounts receivable. Yes, allowance accounts that offset gross receivables are reported under the current asset section of the balance sheet. This type the allowance for doubtful accounts is a contra asset account that equals: of account is a contra asset that reduces the amount of the gross accounts receivable account.
Adjusting the Allowance

This method is particularly useful for businesses with consistent sales patterns and stable customer bases. Regardless of company policies and procedures for credit collections, the risk of the failure to receive payment is always present in a transaction utilizing credit. Thus, a company is required to realize this risk through the establishment of the allowance for doubtful accounts and offsetting bad debt expense. In accordance with the matching principle of accounting, this ensures that expenses related to the sale are recorded in the same accounting period as the revenue is earned. The allowance for doubtful accounts also helps companies more accurately estimate the actual value of their account receivables. On the income statement, the provision for doubtful accounts is recorded as an expense, reducing the net income for the period.
- Companies often have a specific method of identifying the companies that it wants to include and the companies it wants to exclude.
- The sales method applies a flat percentage to the total dollar amount of sales for the period.
- This method, while straightforward, requires regular updates to reflect any changes in the business environment or customer base.
- The risk classification method involves assigning a risk score or risk category to each customer based on criteria—such as payment history, credit score, and industry.
- This will help present a more realistic picture of the accounts receivable amounts you expect to collect versus what goes under the allowance for doubtful accounts.
- For example, our jewelry store assumes 25% of invoices that are 90 days past due are considered uncollectible.
- This method involves applying different percentages to receivables based on their age, as categorized in the aging schedule.
- For example, a company may assign a heavier weight to the clients that make up a larger balance of accounts receivable due to conservatism.
- This will ensure that your financial statements accurately represent the status of your company’s accounts receivable.
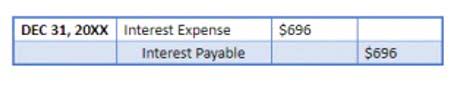
- The accounting journal entry to create the allowance for doubtful accounts involves debiting the bad debt expense account and crediting the allowance for doubtful accounts account.
- Units should consider using an allowance for doubtful accounts when they are regularly providing goods or services “on credit” and have experience with the collectability of those accounts.
You record the allowance for doubtful accounts by debiting the Bad Debt Expense account and crediting the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts account. You’ll notice the allowance account has a natural credit balance and will increase when credited. Assume a company has 100 clients and believes there are 11 accounts that may go uncollected.

 ไทย
ไทย



